Use livestock systems to manage land, water and biodiversity resources sustainably
Livestock can be managed to enhance rather than harm the environment.
Core message
Facts
Well-managed, livestock support sustainable land and water management.
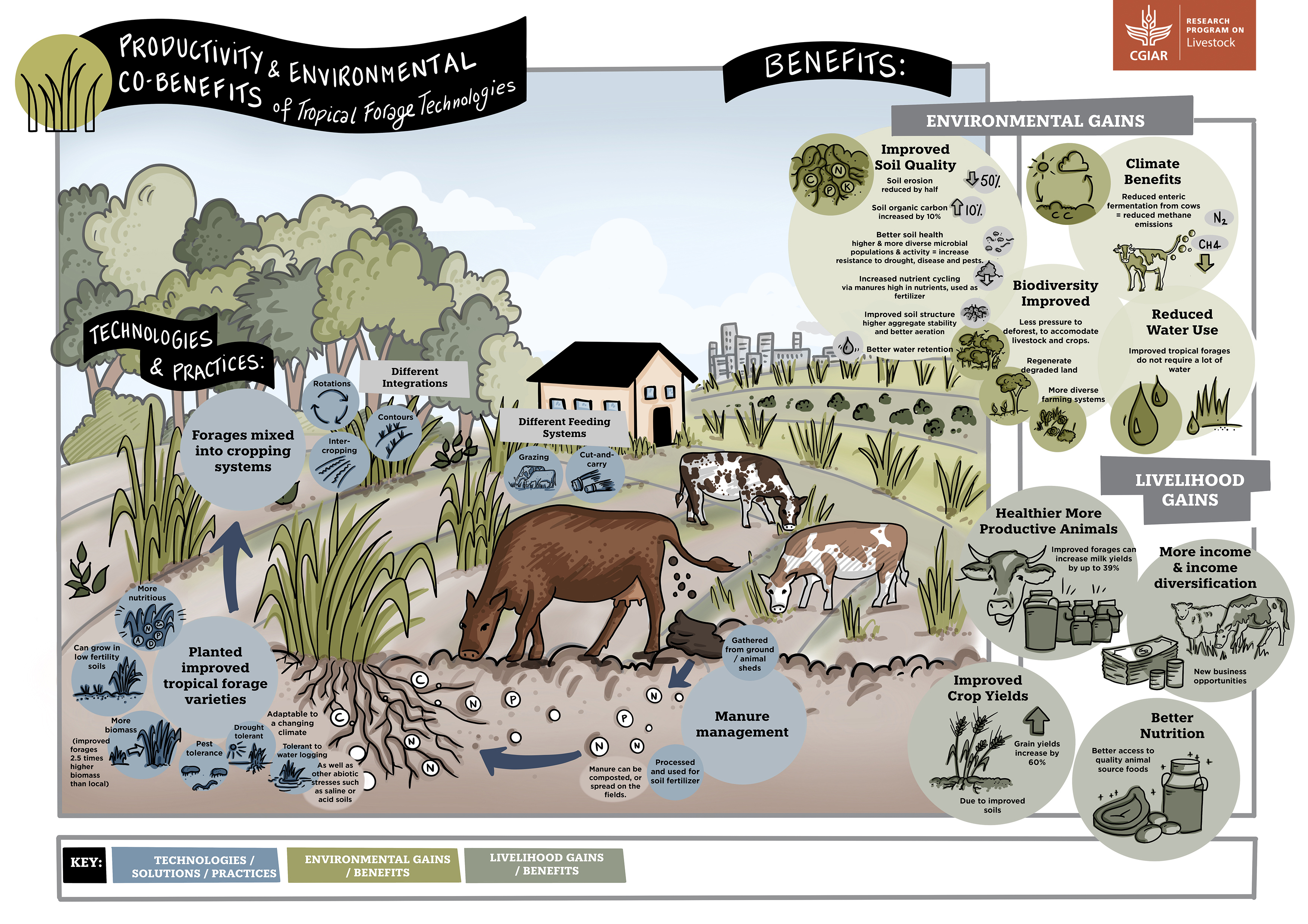
Livestock manure is a ready source of natural organic fertilizer for croplands, providing 12% of the nitrogen used for crop production globally and 23% of that used for crop production on mixed crop-and-livestock farms.
Livestock manure not only helps ‘close nutrient cycles’ by replenishing soils with nitrogen but also enhances soil structure and organic matter, thus improving the nutrient- and water-holding capacities of soils and reducing soil erosion.
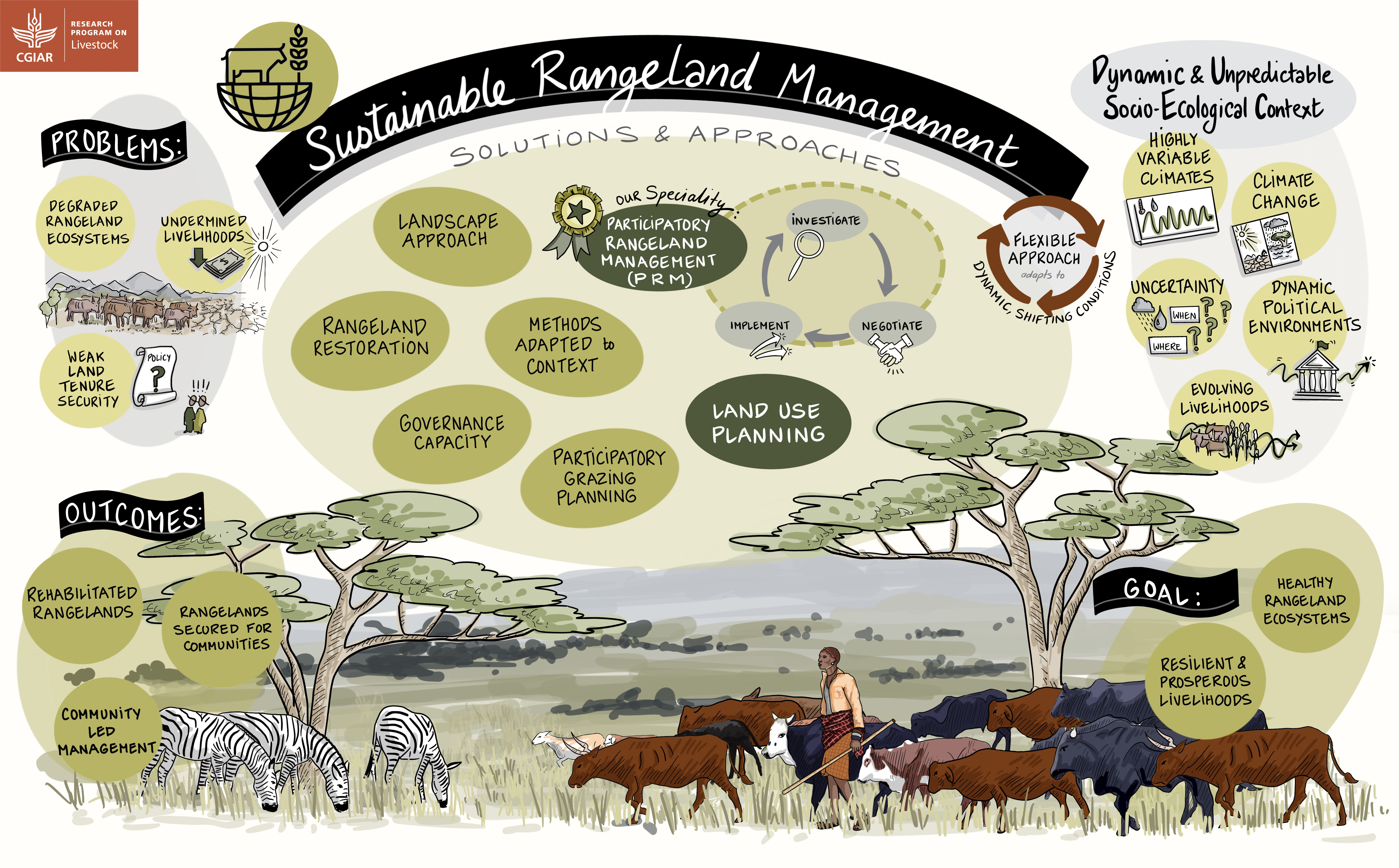
Livestock can help restore degraded lands; livestock raised on rangelands, for example, can promote the biodiversity of plants, animals and soil organisms.
Livestock production systems, and thus options for their environmental and socio-economic sustainability, vary hugely around the world.
Well-managed, cattle and other ruminant animals help renew rangelands; they stimulate healthy growth on semi-arid and marginal lands, for example, thereby significantly increasing carbon sequestration in the soil and vegetation.
Actions
Encourage close livestock-crop integration and interactions.
Make optimal use of resources by, for example, supporting markets selling livestock manure to crop farmers and selling feed in the form of maize stover, rice straw and other crop residues to livestock farmers.
Ensure that government programs aiming to increase agricultural productivity are broad based, covering livestock as well as crops and all the interactions between them.
Tailor livestock practices for specific environments to get the maximum benefit from the natural synergies between livestock and the environment.
Provide livestock keepers in extensive systems with equitable and guaranteed access to lands through better land-use planning and land management incentives that encourage sustainable livestock production.
Support the environmental stewardship provided by the world’s pastoral peoples, which significantly increases carbon sequestration as well as helping to conserve biodiversity.